It has been a very long time since the average computer user thought about .cue files, or cue sheets, the metadata bits that describe the tracks of an optical disc, like a CD or DVD. But cue sheets are getting attention again, for all the wrong reasons. They’re at the heart of a one-click exploit that could give an attacker code execution on Linux systems with GNOME desktops.
CVE-2023-43641, disclosed by GitHub on October 9, is a memory corruption (or out-of-bounds array writing) issue in the libcue library, which parses cue sheets. NIST has yet to provide a score for the issue, but GitHub’s submission rates it an 8.8, or “High.” While the vulnerability has been patched in the core library, Linux distributions will need to update their desktops to fix it.
GNOME desktops have, by default, a “tracker miner” that automatically updates whenever certain file locations in a user’s home directory are changed. If a user was compelled to download a cue sheet that took advantage of libcue’s vulnerability, GNOME’s indexing tracker would read the cue sheet, and code in that sheet could be executed.
Kevin Backhouse / GitHub
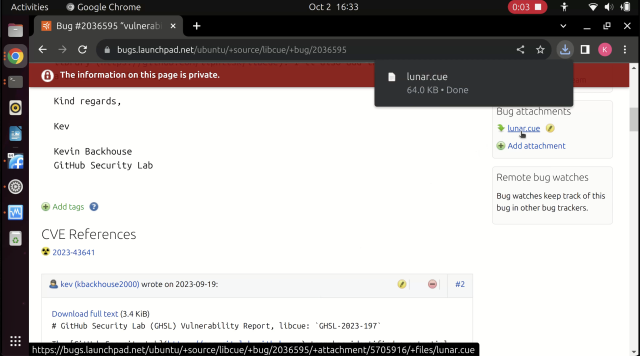
Part one of the .cue-based exploit example: An Ubuntu desktop, with a browser open, downloading a CUE file.
Kevin Backhouse / GitHub
Kevin Backhouse / GitHub
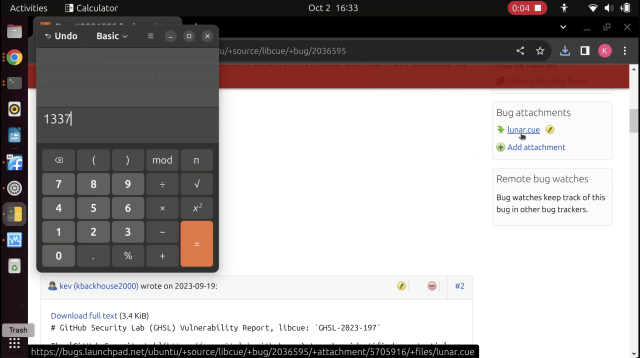
Part 2: A calculator immediately pops up, with “1337” in the numerical display. You can imagine that most exploits would have far worse consequences.
Kevin Backhouse / GitHub
Part one of the .cue-based exploit example: An Ubuntu desktop, with a browser open, downloading a CUE file.
Kevin Backhouse / GitHub
Part 2: A calculator immediately pops up, with “1337” in the numerical display. You can imagine that most exploits would have far worse consequences.
Kevin Backhouse / GitHub
Kevin Backhouse, a member of GitHub’s Security Lab, offers a video demonstration of the exploit in his blog post but has not yet published the proof of concept to allow for patching. You can test your system’s vulnerability against a test cue sheet he offers, which should trigger “a benign crash.”



